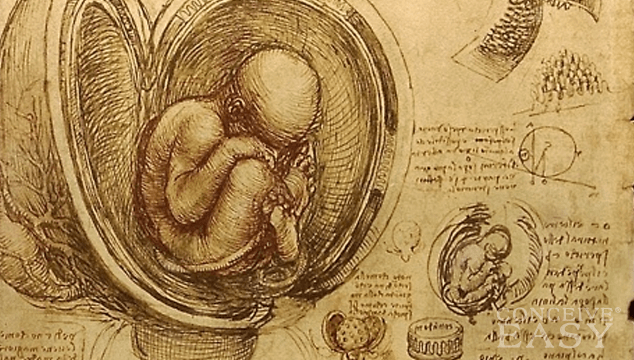
The developmental stages of a baby right from conception to the birth of the child are predictable. Things start as the cells begin to divide. They differentiate and form a zygote. After the formation of the zygote, the blastocyst is formed. It is from the blastocyst that the embryo is formed. Claim Your 20 Free Pregnancy Tests – Click Here
After this, the fetus develops. All these changes occur in the first thirteen weeks of pregnancy itself. Right from the start, the cells require nutrients and oxygen to develop and divide. It is the placenta and the umbilical cord that work as the connecting link between the fetus and the mother. They transfer the nutrition to the baby from the mother.

Placenta is actually a temporary organ. It has membranes and blood vessels and it connects the mother to the fetus. The formation of placenta begins in the blastocyst stage. Blastocyst stage is a stage where there is a hollow ball of cells that implants itself in the uterus.
The cells in blastocyst can be divided as inner cells and outer cells. The inner cells develop to form the embryo while the outer cells fill themselves with blood from the lining of the uterus of the mother. Now blood vessels are formed here.
Thus, a connection is established between the mother and the embryo. Through this connection the embryo’s blood vessels are surrounded by the blood from the mother. Now exchange of oxygen and nutrients is easy.

The placenta has a number of thin tissues and these tissues are together called as the blood barrier. This barrier works to allow the flow of a few particles from the mother to the fetus and vice versa. It also restricts a few other particles.
In other words, it is a semi-permeable barrier. From the mother to the fetus, the placenta transfers nutrients and oxygen. From the fetus, waste products are transferred to the mother. Placenta is also responsible for the production of a few hormones such as the hCG or human chorionic gonadotropin, progesterone, and estrogen. These hormones work to tell the mother’s body about the needs of the baby. Alongside, the placenta is important because it works to protect the fetus from white blood cells, red blood cells of the mother and other harmful particles. These are harmful because they will treat the baby as a foreign substance or invader and attack it.

Placenta is also the source of nutrition for the baby because it transfers nutrition from the mother to the baby. When the mother eats food, it is broken down by the digestive system into absorbable particles. These particles are absorbed into the bloodstream.
These nutrients travel from the bloodstream of the mother into the bloodstream of the fetus thanks to the placenta. In the same way the fetus absorbs fat, protein, and calcium, which are obtained through the breaking down of bones, fat, and muscles.

You may wonder how the placenta and the embryo are connected. They are connected through a stalk like structure that later forms the umbilical cord. With the growing fetus, the stalk grows and develops a vein and two arteries. When the gastrointestinal system of the baby is developed, the stalk protrudes through a structure called the umbilical ring and this is when it develops into the umbilical cord.








Comments