Abnormal ovulation (rare ovulation or absence of it) is a main cause of female infertility. Fertility drugs for women are widely used to treat a variety of fertility problems, such as endometriosis and polycystic ovary syndrome, as well as various ovulation problems, thus enhancing the chances of becoming pregnant. Claim Your 20 Free Ovulation Tests – Click Here
Many such drugs are prescribed for the purpose of treating irregular ovulation or lack of ovulation altogether (anovulation), a medical condition denoting the inability to release eggs. Especially as a woman gets older, her egg health begins to deteriorate, so it may be best to help stimulate ovulation, to help release multiple eggs sometimes to try to have ready that single ‘good egg’ that will get you pregnant. The 4 most common types of ovulation medication are:
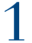
Clomiphene citrate pills is the medication of choice to stimulate ovulation and thus optimize your chances of conceiving. Clomid for short. It targets the pituitary gland and determines it to produce and release more follicle-stimulating hormones (FSH), leading to the growth of estrogen-secreting ovarian follicles and the release of the luteinizing hormone (LH). Thus, the ovulatory phase of the menstrual cycle begins, and this is the optimum moment to try to conceive. 36 hours later, ovulation occurs when the dominant ovarian follicle releases its fully matured egg.
Often, the doctor will adjust the initial dosage of Clomid. This drug is usually prescribed for at least three consecutive menstrual cycles. It is well-tolerated, it has mild side-effects and shows results in 80% of the treated women. However, note that women suffering from ovulation problems arising from hypothalamic disorders and extremely low estrogen levels do not respond well to Clomid.

Gonadotropin injections are usually prescribed for women suffering from lack of ovulation and who did not respond to the clomiphene treatment. This medication determines the stimulation of FSH and LH, to result in the development of a fully matured ovarian follicle, accompanied by a proper estrogen level. At this point, the ovulation is induced with the aid of Human chorionic gonadotropin. Typically, ovulation takes place about 36 hours after this injection.
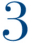
Follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone and human menopausal gonadotropin injections are synthetic hormones that mimic the presence of the natural ones. They balance the estrogen levels and help to induce ovulation in women who rarely or never ovulate.

Bromocriptine and Cabergoline pills work by suppressing the pituitary gland’s production of prolactin, which interferes with the production and release of FSH and LH, and thus inhibits ovulation. The use of these drugs induces ovulation in 85% of the women treated, in the absence of other infertility issues.
Other ovulation medication include injections with Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), GnRH agonists and GnRH antagonists, dopamine agonists and insulin-sensitizing agents, all prescribed for ovulatory dysfunctions and having specialized uses.
Most fertility problems related to irregular or absence of ovulation are successfully treated with the use of such drugs. The specific cause should be determined by a thorough medical evaluation prior to administering the right medication.









Comments