In spite of many fertility drugs and supplements being available, some women need a lot more help in order to conceive a child. Certain medical procedures, consisting of fertilizing the egg using special laboratory techniques and instruments, are used in order to offer those patients a chance to get pregnant. Claim Your 20 Free Pregnancy Tests – Click Here
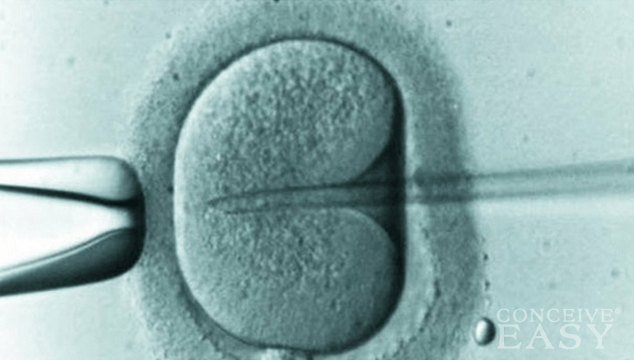
All these procedures are known under the generic name of assisted reproductive technologies, and have a success rate that ranges between 29% and 50%. Besides in vitro fertilization (IVF), GIFT and ZIFT are two of the most commonly used methods of assisted reproduction. Here is a brief presentation of the two methods.

Gamete Intra-Fallopian Transfer (GIFT) is simpler to perform than IVF, and it puts less pressure and stress on the couple who wants a child. The woman who undergoes the procedure must have both fallopian tubes perfectly healthy, while in vitro fertilization can be performed even if these organs are absent.
GIFT is performed under general anesthesia, and, although such cases are very rare, this can cause some complications. This procedure does not involve any process that takes place outside the patient’s body, the fertilized eggs being injected directly in the fallopian tubes, without any lab-developed embryo culture being necessary.
The main purpose of GIFT is to allow the embryo to form and grow in the place where it belongs, in a manner that is close to the natural process. The success rate of this procedure is situated around 29%, a similar level with that of the successful IVF cases.

Zygote Intra-Fallopian Transfer (ZIFT) is an assisted reproduction technique that is mainly recommended to women over 40 years of age, who are not able to get pregnant in any other way. The existence of at least one healthy fallopian tube is an essential condition for the success of the procedure.
It involves extracting the egg from the ovaries, fertilizing it in the laboratory, and implanting the formed embryo into the patient’s fallopian tube, after it is kept in laboratory under observation for a period of 24 hours.
The transfer of the zygote is made using laparoscopic instruments, and the patient is under the influence of general anesthesia. The success rate of this procedure is greater than in cases of IVF and GIFT, being situated around 32%.
In a way, GIFT and ZIFT are pretty similar, except that, in the first case, the embryo develops in the uterus, the laboratory stage being skipped.








Comments